Astronomy 101
A Glossary of Astronomy Terms & Interesting Facts
Asteroids: Sometimes called planetoids, asteroids are objects in the Solar System that are smaller that a planet or a planet's moon. Asteroids are thought to be fragments of much larger bodies that broke apart early in the life of a Solar System.
The asteroid pictured here is one of the largest asteroids in our Solar System, some 326 miles (525 km) wide. It was first discovered in 1807 and has been named Vesta.
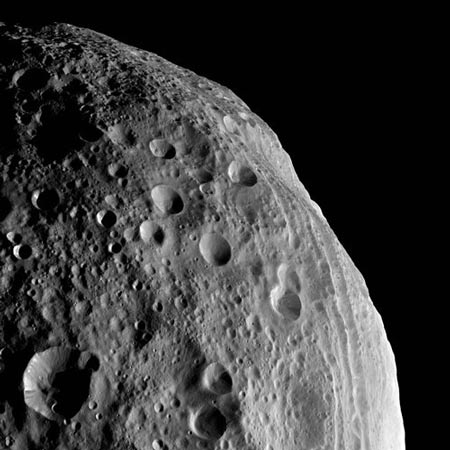

The asteroid pictured here is one of the largest asteroids in our Solar System, some 326 miles (525 km) wide. It was first discovered in 1807 and has been named Vesta. The image you see was photographed from NASA's Dawn Spacecraft, which orbited Vesta for one year to study its features. Vesta is believed to have an iron-nikel core. Photo credit: NASA/Dawn Spacecraft
If Vesta were to become Earth-bound and slam into our planet (which it never will), it would unquestionably wipe out all life on Earth. The dinosaur-killing meteor that crashed off the Yucatan Peninsula 65 million years ago was only 6 miles in diameter. Currently, NASA is tracking more than 600,000 Earth-bound asteroids — asteroids that travel close to Earth. When an asteroid large enough to do damage is detected, NASA's Near Earth Object Program Office will work to divert the asteroid, most likely by nudging it harmlessly toward the Sun.
Amazing Asteroid Facts:
There are hundreds of millions of nearby asteroids the size of a car; one of these enters the Earth's atmosphere about every 8 months.
There are 1.3 million nearby asteroids the size of a 100-ft yacht; one enters the atmosphere every 200 years or so.
There are 20,000 nearby asteroids the size of a Giza pyramid; one of these enters Earth's atmosphere every 13,000 years and explodes with the intensity of 8,600 Hiroshima blasts.
There are 1,000 nearby asteroids the width of 12 New York City blocks; one will enter our atmosphere every 440,000 years and explode with the force of 3 million Hiroshima blasts.
There are 4 nearby asteroids as wide as the city of Miami; they enter our atmosphere about once every 89 million years with a force of 3 billion Hiroshima blasts.
Source: Donald H. Yeomans, Near Earth Object Progam Officer
Comets: A temporary visitor to the Solar System that falls towards our Sun from a cloud of comets at the edge of the Solar System. Comets are thought to be "dirty snowballs". They can form a tail when their gases are warmed as they approach the Sun. Comets are icy, whereas asteroids are rocky.
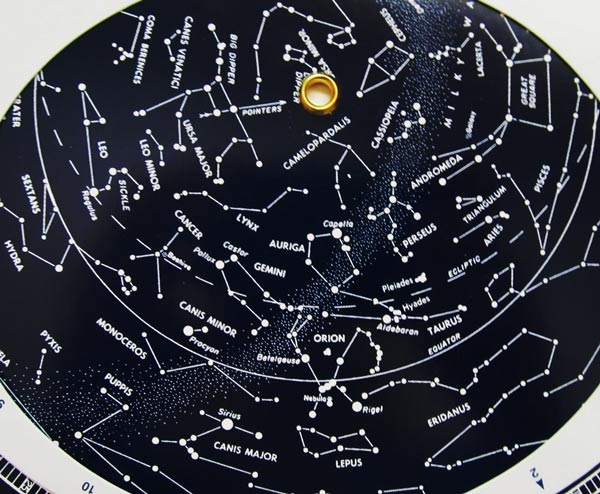

Planispheres, such as the one pictured here, display constellations that move across our night sky. Photo credit: WPO
Constellations: An association of stars appearing as a recognizable figure in the night sky. Star charts connect stars into patterns, but astronomers use coordinates similar to latitude and longitude to find their way in the night sky.
Galaxy: A giant aggregate of billions of stars, interstellar gas, and dust. The history of the observation of star systems outside our Milky Way galaxy dates back to the Persian astronomer Abd-al-rahman al-Sufi, who in 964 AD made note of the Andromeda Galaxy, which he described as "a little cloud". But it was not until 1924 that it could be proved beyond a doubt that this brightest of all galaxies is, in fact, an entire island universe outside the Milky Way.
How many galaxies are there in the visible universe? Astronomers aren't exactly sure. There are limitations in their instrumentation, so the estimates vary widely. As of 2014, astronomers guesstimate that there are between 100 billion and 200 billion galaxies.
How many stars are there in a galaxy? From 10 million to 100 trillion, depending on the size of the galaxy.
If we do the math, this means that there are as many as 1024 stars in the visible universe, or:
1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 stars.
Every speck and smudge in the picture below, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, is an entire galaxy! This massive slice of the universe, when looked at in our night sky, is no wider than the diameter of a dime.
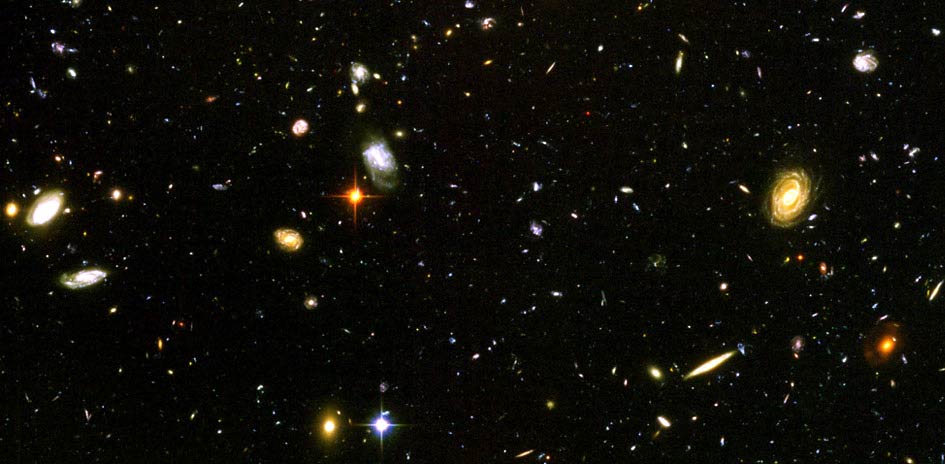

Photo credit: Hubble Space Telescope
Galileo: Galileo is the first man recorded to have used a telescope to observe objects that are not on the Earth. The four primary moons of Jupiter are named the Galilean moons because Galileo's telescope was the first to spot them.
Magnitude: The brightness of stars is rated in orders of magnitude. A star with a magnitude rating of "1" falls in the brightest star category. A second magnitude star is half as bright. Distant galaxies, which only the most powerful telescopes can see, are as low as 14th magnitude.
Nebula: Stars are born in diffuse nebulae made up of doubly ionized hydrogen gas, which is the building blocks of stars. Star-bearing regions, also known as stellar nurseries, are some of the closest objects to us in the Milky Way. The Orion Nebula, pictured below, is a nearby stellar nursery. It is visible to the naked eye as the third "star" in Orion's scabbard. Learn how to see Orion from your own back yard.
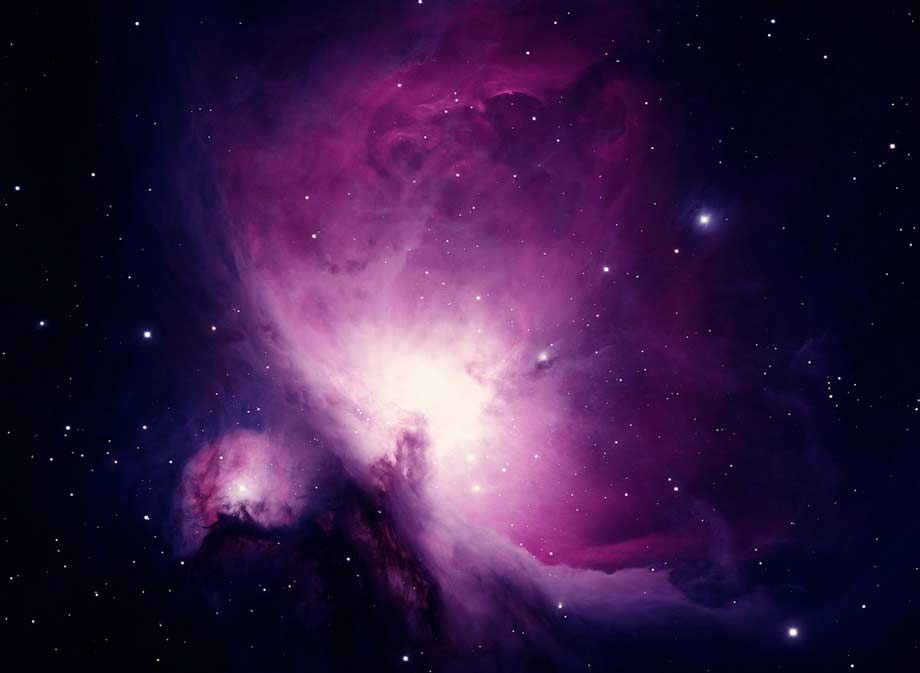

Photo credit: NASA
A NEWTON RIDDLE:
What do the bubonic plague, a nervous breakdown, and failing as a farmer have to do with the greatest scientific publication of all time?
the answer
Newton, Isaac: Renaissance scientist par excellance, Isaac Newton invented the first telescope to use mirrors, in addition to his renowned laws of gravity. These laws describe the celestial mechanics of a pre-Einstienian Universe commonly referred to as the "Newtonian Universe". It is the Laws of the Newtonian Universe that made manned space travel possible.
Newtonian telescope: Isaac Newton invented the reflecting telescope which consists of a primary mirror focusing a cone of light into a secondary mirror through which an image can be viewed at an eyepiece.
Planet: A non-stellar body which orbits a star and shines from the light it reflects from that star. The weather on planets in our own Solar System is visible from Earth based telescopes like Windowpane Observatory. Planets have satellites or moons much like the Earth's moon. Planets are also visible from Earth-based telescopes. The first person to see the brightest moons of Jupiter was Galileo.
Planets that revolve around stars other than our own Sun are called exoplanets or exosolar planets. Astronomers have discovered that many exoplanets live in what is called a 'habitability zone' and have all the right conditions for harboring life. Some of the suns of these planets can be seen with the naked eye in our own night sky. Learn about these nearby extraterrestrial worlds.
Short-focus telescope: A short-focus telescope is a telescope whose focal ratio is small. A small focal ratio causes a reflecting telescope to be physically shorter that a long focus telescope. A shorter focal ratio means that objects are bigger and brighter when observed.
Short-term event: Short-term astronomical events are transient phenomena occurring in the skies over a brief period of time. The passing of a comet is an example of a short-term event.
Sonoran Desert: The Sonoran Desert extends up from Northern Mexico into Southern California and Arizona. Known for its dry, clear climate, the Sonoran Desert is resplendent with observatories such as Palomar and Kitt Peak. Eighty miles southwest of Kitt Peak is Windowpane Observatory in Ajo, Arizona; gateway to Organ Pipe National Monument and part of a United Nations protected biosphere. This pristine desert is home to many unique species of plants and animals and is a mecca for wildlife biologists.
Supernova: A supernova is the remnant of a dying star and may be called a stellar gravesight, just as nebulae are stellar nurseries where new stars are born.
When a star reaches the end of its life it collapses upon itself. This implosion results in an explosion. If the star novas a gas still visible in telescope marks the gravesight. If the star supernovas this explosion is visible across hundreds of millions of light years of space. A supernova may leave massive clouds of glowing gas visible from Earth. When photographed with special filters, the various types of gasses take on hues of color.
One of the most famous supernovas is the Helix Nebula, pictured below.
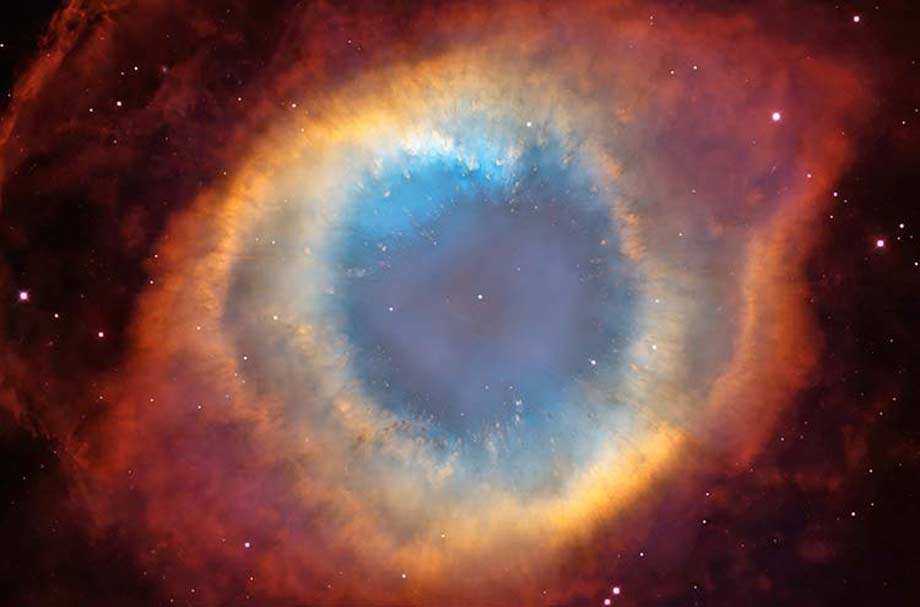
Photo credit: NASA
Visual Observatory: An observatory like Windowpane Observatory where astronomy is performed in the tradition Galileo and Isaac Newton. In a visual observatory, the human eye, not electronic instruments, is relied upon. Visual astronomy is relegated to the science of discovery where quick observation with the human eye can reveal the presence of new comets, stars exploding inside galaxies (supernovae) or new asteroids coming close to the Earth.
 See an animation of the movement of planets in our solar system.
See an animation of the movement of planets in our solar system. See amazing views from space
See amazing views from space